ALKANES
The alkanes are acyclic saturated
organic compounds made up of carbon and hydrogen only. These compounds are
fully saturated, have only a single bond in the whole molecule. These are also known
as hydrocarbons because these are consisting of only carbon and hydrogen.
Another name of an alkane is
paraffin because alkanes are fully saturated with only a single bond present in a
molecule that’s why have a very low affinity for different reactions, so they are
less reactive compounds. They contain no double or triple bond in their
molecules and have only a single covalent bond in the whole molecule.
Properties of alkanes
1. Alkanes are less
reactive due to their saturated nature.
2. The name of
alkanes ends with –ane.
3. The general
formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2, where n shows the number of
carbon atoms present in a molecule.
4. The smaller
member of the alkane class is gases but the higher members exit as liquid and solids.
5. The melting and
boiling point of alkanes increase with the increase of the number of carbon atoms
in compounds.
6. They have only
C-C single bond in a molecule and no double or triple bond is present.
7. The compounds
which are present in solid form have a waxy texture.
8. These are
non-polar compounds, so they dissolve only in non-polar solvents.
9. These compounds
are colorless and odorless.
Preparation of alkanes
Alkanes are
prepared by different methods which are as follows.
·
Hydrogenation of
alkene or alkyne
Hydrogenation is processed in
which hydrogen is added in an alkene and alkynes in the presence of nickel and
high pressure and temperature. This process can also be carried out in the
presence of platinum or palladium
 |
| hydrogenation |
·
From Grignard
reagent
The Grignard reagent reacts with water or dilute acid and is converted into different alkanes.
 |
| from Grignard reagent |
·
By decarboxylation
The process during which carbon dioxide is removed from the salt of a carboxylic acid is known as decarboxylation. This process is carried out in the presence of slaked lime with sodium hydroxide and
heat.
 |
| decorboxylation |
·
By reducti
When alkyl
halide reacts with Zn in the presence of acid halides it produces different types
of alkanes.
 |
| alkyl halide |
·
Wurtz reaction
In this reaction, two molecules of
alkyl halide react with sodium in the presence of ether and heat. Symmetrical
alkanes with an even number of carbon atoms are formed during this reaction.
· From carbonyl compounds
The carbonyl group
of aldehyde or ketone is reduced to a methyl group and produces a different type of
alkanes. Two types of reduction occur in carbonyl compounds.
1.
The reduction of ketone in the presence of zinc amalgam
and Hcl is known as Clemmensen’s
reduction.
2. The reduction of an aldehyde with hydrazine in the presence of potassium hydroxide is known as wolf-Kishner’s reduction.
 |
| from carbonyl compounds |
·
From alcohol and carbonyl compounds
The reduction of alcohol and carbonyl compounds in presence of red P & HI gives the corresponding alkane.
·
From carbide
Alkanes can also
be prepared by the reaction of water with metal carbide.
Reactions of alkanes
Alkanes are less reactive as
compared to alkene and alkyne due to their saturated nature, under high
conditions it undergoes following reactions.
1. Combustion
The reaction of alkane with
oxygen is known as combustion. When alkanes are completely burned during this reaction then carbon dioxide and water are formed.
This reaction is highly exothermic because a large amount of heat is released
during the reaction.
 |
| combustion |
2. Halogenation
The addition of halogens in alkanes is known as halogenation. Alkanes react with
different halogens in different conditions. They react with chlorine and bromine
in sunlight or high temperature but the reaction with fluorine is very violent
and result in mixtures of products. Iodine does not react directly with alkanes
because the reaction is reversible and too slow.
Halogenation is carried out by free
radicle reaction, consist of series of events and result in different types of
products. These reactions have three steps;
·
Initiation
·
Propagation
·
Termination
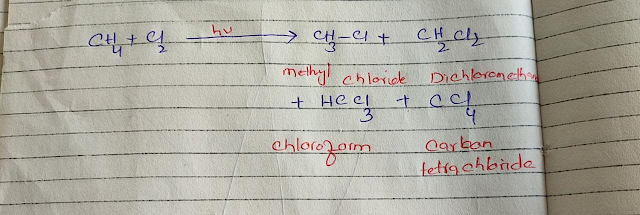 |
| halogenation |
3. Nitration
The addition of the nitro group in
alkanes is known as nitration. This reaction occurs in the vapor phase and under
high temperatures. In this reaction, alkane reacts with nitric acid at high temperature.
 |
| nitration |
4. Oxidation
The reaction of alkanes with
oxygen gives different products in different conditions. The incomplete oxidation
of alkanes gives different products that are CO and water and carbon black.
In catalytic oxidation, different
products are formed in the presence of a catalyst and high temperature and
pressure. The catalyst used in this reaction is copper.
 |
| oxidation |
Uses of Alkanes
![]() Alkanes are used as the main constituent of gasoline and lubricating
oil.
Alkanes are used as the main constituent of gasoline and lubricating
oil.
![]() Alkanes are present in natural gas used for cooking
and heating purposes.
Alkanes are present in natural gas used for cooking
and heating purposes.
![]() They are also used for the manufacturing of urea
fertilizers.
They are also used for the manufacturing of urea
fertilizers.
![]() We can also use alkanes as a fuel and as an
illuminating gas.
We can also use alkanes as a fuel and as an
illuminating gas.
![]() They are also used as raw material for the preparation
of different compounds in the chemical industry.
They are also used as raw material for the preparation
of different compounds in the chemical industry.
![]() The carbon black used in automobiles tyres is also
prepared from alkanes.
The carbon black used in automobiles tyres is also
prepared from alkanes.
.











0 Comments
Thanks for visiting blog. if you have any query please let me know.