What is alcohol?
Alcohol is a class of acyclic organic compounds made up of
carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. Alcohols are considered derivatives of water.
When we replace one hydrogen of water with an alkyl group then alcohol is formed.
Alcohol has a close resemblance with phenol class because both have the same
functional group ( hydroxyl group –OH ).
On the basis of a number of no of hydroxyl group present in a compound they are designated as mono, di, tri, or polyhydric alcohol. Monohydric alcohol is further classified into three types:
·
Primary alcohol
If the hydroxyl group attached to that carbon atom
which is further attached to one more carbon atom or no carbon atom, this compound is known as primary alcohol.
·
Secondary
alcohol
If the hydroxyl group attached to that carbon atom
which is further attached to two more carbon atoms, than this compound is known as
secondary alcohol.
·
Tertiary
alcohol
If the
hydroxyl group attached to that carbon atom which is further attached to three more carbon atoms, then this compound, is known as tertiary alcohol.
Physical properties
of alcohol
- 1.
The trivial name of alcohol is alkyl alcohol.
- 2.
The general formula of alcohol is R-OH.
- 3. Alcohols
are polar molecules, due to the presence of hydroxyl group so they are easily
dissolve in water. They are able to make hydrogen bonding with water, but this
ability decreases in higher alcohols
- 4. Lower
member of alcohol are colorless toxic liquids that have burning taste and
sweat smell.
Methods for the preparation of alcohol
Alcohols are
prepared by different methods which are as follow:
v Hydration of alkene
When hydrolysis of
alkene is carried out then alcohol is formed in this reaction.
v Hydrolysis of alkyl halide
When alkyl halides react with an aqueous solution of potassium hydroxide, alcohol is formed in this reaction by nucleophilic substitution reaction.
 |
| hydrolysis of alkyl halide |
- preparation on an industrial scale
Methanol is
prepared on an industrial scale by the distillation of wood. The other name of
methanol is wood spirit. It is prepared from CO and hydrogen.

Preparation of alcohol on an industrial scale
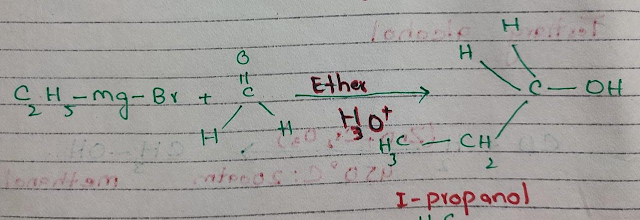
v Reaction of the Grignard reagent with aldehyde or ketones
When Grignard reagent
reacts with carbonyl compounds in the presence of ether the resulting product
is alcohol.
v From starch
When starch
reacts with water in the presence of the diastase enzyme in yeast, it is converted
into maltose. When fermentation of
Maltose is carried out in the presence of the maltase enzyme in
yeast, it is converted into glucose. Glucose is converted into alcohol in the
presence zymase enzyme in yeast.
But alcohol obtained through fermentation very
little, only 12 to 14%. This obtained alcohol is distilled again and again to
obtain 95% alcohol. This alcohol is known as rectified spirit.

preparation of alcohol from starch
v From molasses
When the fermentation
of molasses in the presence of the Zymase enzyme in yeast is carried out then alcohol is formed. Molasses
is a residue that is obtained after the crystallization of sugar from the con. Sugar
can juice.

preparation of alcohol from molasses
v Reduction of carboxylic acid
When reduction of a carboxylic acid is carried out then alcohol is formed. This reduction occurs in very strong reducing an agent that is Lithium aluminum hydride in ether.
Reactions of alcohols
The reaction of alcohol with other compounds occurs in two ways.
1.
Reaction
in which O-H bond break
2.
Reaction
in which C-O bond break
Which the bond will break in a reaction, it depends upon the attacking reagent, if any
electrophile attack on alcohol then O-H will break. If nucleophile attacks on
alcohol then the C-O bond will break.
1. Reaction
in which O-H bond break
The
reaction in which O-H bond break is as follow:
Ø Reaction with sodium
Alcohol reacts with sodium and form
sodium ethoxide.
- Reaction with Grignard reagent
Alcohol reacts with the Grignard reagent
to form alkane.

reaction of alcohol with Grignard reagent
- Reaction with acetic acid
Alcohol reacts with acetic acid to
ethyl acetate.
|
2. Reaction
in which C-O bond break
The reactions in which the C-O bond breaks
are as follow:
Ø Reaction with hydrochloric acid
When alcohol reacts with hydrochloric acid then alkyl
halides are formed.
 |
| ethyl chloride |
Ø Reaction with thionyl chloride
When alcohol reacts with
thionyl chloride then alkyl halides are formed.

Reaction of alcohol with thionyl chloride
Ø Reaction with nitric acid
When alcohol reacts with
nitric acid then ethylamine is formed.
3.
Other reactions
of alcohols
Alcohols
also, give some other reactions.
Ø Dehydration of alcohol
When alcohol
reacts with con. H2SO4 then it gives different products
on different temperatures.
Ø Reaction with PCl3, PCl5
Alcohol reacts
with PCl3, PCl5 to form alkyl halides.
Ø Oxidation reaction of alcohol
When oxidation of alcohol is carried out
then ketones and aldehyde are formed. Acid dichromate reagent is used in this
reaction.
Uses of Alcohols
 Ethanol is used as a solvent, fuel in many countries,
and as a drink.
Ethanol is used as a solvent, fuel in many countries,
and as a drink. Ethanol is also used as a preservative in biological
specimen.
Ethanol is also used as a preservative in biological
specimen. Methanol is used as an antifreeze in the radiator of
automobiles.
Methanol is used as an antifreeze in the radiator of
automobiles. Methanol is also used for denaturing alcohol.
Methanol is also used for denaturing alcohol. Alcohols are used as solvents for varnishes and paints.
Alcohols are used as solvents for varnishes and paints. Ethanol is also used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Ethanol is also used in the pharmaceutical industry.















0 Comments
Thanks for visiting blog. if you have any query please let me know.