In this article i briefly discuss about the mass spectrometry
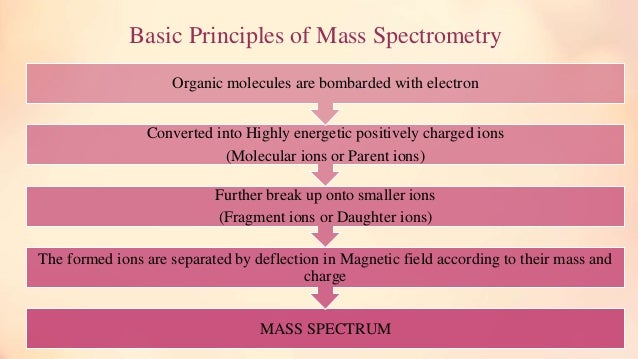
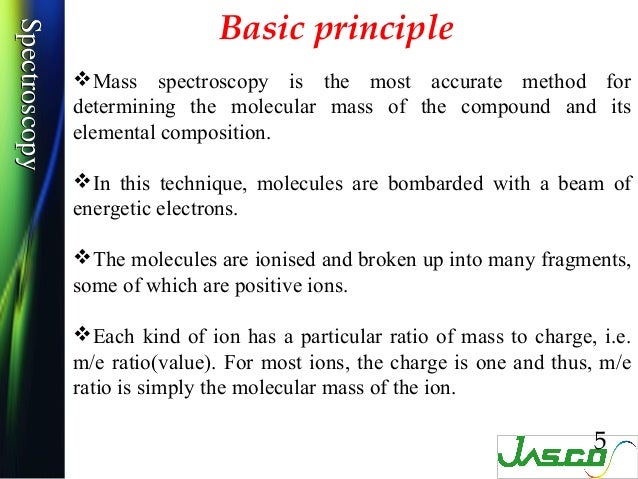

- Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that utilize the degree of deflection of charged particles by a magnetic field to find the relative masses of molecular ions and fragments.
- It is a powerful method because it provides a great deal of information and can be conducted on tiny samples.
- Mass Spectrometry is a powerful technique for identifying unknowns, studying molecular structure, and probing the fundamental principles of chemistry.
- Mass spectrometry is a powerful analytical technique used to quantify known materials, to identify unknown compounds within a sample, and to elucidate the structure and chemical properties of different molecules.
- Mass spectrometry’s characteristics have raised it to an outstanding position among analytical methods: unequalled sensitivity, detection limits, speed and diversity of its applications.
- Mass spectrometers use the difference in mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ionized atoms or molecules to separate them. Therefore, mass spectroscopy allows quantitation of atoms or molecules and provides structural information by the identification of distinctive fragmentation patterns.
- Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measure the mass to charge particle.It is used for determing the mass of particles, for determining the elemental composition of sample or molecule.
- Mass spectrometry is ananalytical technique that helps identify the amount and type of chemical present in a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions.
History of mass spectrometry
- In the 1890s when J. J. Thomson determined the mass-to-charge ratio of the electron, and Wien studied magnetic deflection of anode rays and determined the rays were positively charged. Each man was honored with the Nobel Prize (Thomson in 1906 and Wien in 1911) for their efforts.
- In 1912–1913, J. J. Thomson studied the mass spectra of atmospheric gases and used a mass spectrum to demonstrate the existence of neon-22 in a sample of neon-20, thereby establishing that elements could have isotopes.
- The earliest mass spectrometer, as we know it today, was built by A. J. Dempster in 1918..
- Development of ionization techniques for high molecular weight (MW) compounds and biological samples in the 1980s and 1990s introduced mass spectrometry to a new community of researchers.
Principle of mass spectrometry

A mass spectrometer generates multiple ions from the sample under investigation, it then separates them according to their specific mass-to-charge ratio (m/z), and then records the relative abundance of each ion type.
The first step in the mass spectrometric analysis of compounds is the production of gas phase
ions of the compound, for example by electron ionization:
M + e− −→ M•+ + 2e−
This molecular ion normally undergoes fragmentations.
M⋅+ EE+ EVEN ION R⋅ RADICAL
OE⋅+ ODD ION N MOLECULE
These two types of ions have different chemical properties.All these ions are separated in the mass spectrometer according to their mass-to-charge ratio, and are detected in proportion to their abundance.A mass spectrum of the molecule is thus
produced. It provides this result as a plot of ion abundance versus mass-to-charge ratio.
The MS principle consist of ionizing chemical compound to generate chemical molecules or molecular fragment and measurement of their mass to charge ratio by using the one of a variety of technique
The general operation of a mass spectrometer is:
1. create gas-phase ions
2. separate the ions in space or time based on their mass-to-charge ratio
3. measure the quantity of ions of each mass-to-charge ratio.








0 Comments
Thanks for visiting blog. if you have any query please let me know.